Difference between revisions of "Thync"
(corr.ref.7) |
(corr.ref.6) |
||
| Line 120: | Line 120: | ||
However, the product is very new, so you can not assume that in the future no health risks to come. Although the technology of neural stimulation of the brain appears to be very dangerous, it is already commonly used for treatment of various diseases. For example: | However, the product is very new, so you can not assume that in the future no health risks to come. Although the technology of neural stimulation of the brain appears to be very dangerous, it is already commonly used for treatment of various diseases. For example: | ||
| − | ''"Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is the application of electric current through the skin to alleviate pain. Among the simple nonpharmacological means, combining psychological and somatic effects and helps reduce the need for analgesics. Most leads to relief of back pain in the suprapubic and perineal relief is smaller. Induces a placebo effect. TENS is a contraindication pacemaker." | + | ''"Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is the application of electric current through the skin to alleviate pain. Among the simple nonpharmacological means, combining psychological and somatic effects and helps reduce the need for analgesics. Most leads to relief of back pain in the suprapubic and perineal relief is smaller. Induces a placebo effect. TENS is a contraindication pacemaker."<ref name="ref6">''PORODNICE.CZ: Transkutánní elektrická nervová stimulace (TENS)'' [online]. Copyright (c) 2002-2015, Porodnice.cz [retr. 8.11.2015]. Available from: http://lekari.porodnice.cz/transkutanni-elektricka-nervova-stimulace-tens</ref> |
Another example is Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS). Deep brain stimulation is based on the transmission of electrical impulses to the brain using thin electrodes. These lead to the neurostimulator which patients are implanted into the chest. Patients with Parkinson's disease, where failed all available therapies, there is a significant motor improvement. Similarly successful this method in patients with epilepsy, which greatly reduces the frequency of epileptic seizures. However tested in people with psychiatric disorders or obesity, said Milan Brázdil, head of the First Department of Neurology at the University Hospital St. Anna in Brno.<ref name="ref7">''ČT24: "Na operace mozku jsme ideálně připraveni", říká Milan Brázdil'' [online]. © Česká televize 1996 – 2015 English [retr. 8.11.2015]. Available from: http://www.ceskatelevize.cz/ct24/archiv/1041312-na-operace-mozku-jsme-idealne-pripraveni-rika-milan-brazdil.</ref> | Another example is Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS). Deep brain stimulation is based on the transmission of electrical impulses to the brain using thin electrodes. These lead to the neurostimulator which patients are implanted into the chest. Patients with Parkinson's disease, where failed all available therapies, there is a significant motor improvement. Similarly successful this method in patients with epilepsy, which greatly reduces the frequency of epileptic seizures. However tested in people with psychiatric disorders or obesity, said Milan Brázdil, head of the First Department of Neurology at the University Hospital St. Anna in Brno.<ref name="ref7">''ČT24: "Na operace mozku jsme ideálně připraveni", říká Milan Brázdil'' [online]. © Česká televize 1996 – 2015 English [retr. 8.11.2015]. Available from: http://www.ceskatelevize.cz/ct24/archiv/1041312-na-operace-mozku-jsme-idealne-pripraveni-rika-milan-brazdil.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 20:25, 8 November 2015
| Thync | |
|---|---|
|
|
| Category | Other Head-mounted Devices |
| Developer | Thync |
| Announced | October 2014 |
| Released | Developers: June 2015
Consumers: June 2015 |
| Price | 299 USD (2015) |
| Operating system | the Thync App on a compatible iOS 8 device (iPhone/iPod). Android App coming in 2015 |
| Sensors | Bluetooth® 4.0 BLE, Single color LEDs indicate power, charge states and current status |
| Weight | Device: 18 g |
| Controls | the Thync App on a compatible iOS 8 device (iPhone/iPod). Android App coming in 2015 |
| Data available | October 2015 |
| Risk factor | risk-free |
| Not standalone[1] | |
| http://www.thync.com/ | |
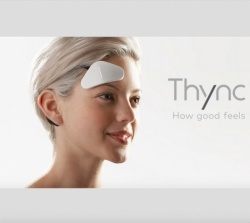
Thync is a small triangular-shaped device that you put on the wearer's head. Headset then stimulates and activates nerves that you either relaxed or energized. Brain neurons remain intact, the device only released electrical impulses. The effect is to remind stimulation massages, only more focused on your head. Thync should help with sleep problems, for example, or the motivation to exercise, to replace the morning coffee and the like.[2]
Thync itself is wireless, connecting to your smartphone or tablet via Bluetooth (it's iOS only at launch, with an Android app coming by the end of 2015). You control Thync from the official app, where you can choose the length of your session. You can also adjust the strength of the brain-zapping there (each program follows a pattern of greater and lesser intensity, with cycles of peaks and valleys, but you can also manually raise or lower the overall strength).[3]
The Company Thync was withdrawing for manufacturing of this device with the same name $ 13,000,000 in October 2014. From 02.06.2015 the equipment is already publicly available. You can buy it from the price of $ 299 (= 7300 CZK).”[2]
Contents
Main characteristics
A soothing neck massage. A splash of cold water. A kiss from someone you love. Each action influences peripheral nerves in your head and face, signaling brain regions to change the way you feel. Thync works using the same pathways by delivering low-level electrical pulses to these nerves. Every day, your body balances the activity between your sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. The sympathetic system is associated with a "fight or flight" response to help regulate your reaction to stress. The parasympathetic system counteracts stress to help you enter a relaxed "rest and digest" mode.[4]
Thync uses neurosignaling to activate specific cranial and peripheral nerves to influence this balance and shift you to a state of calm or give you a boost of energy in minutes. Neurosignaling is the coupling of an energy waveform to a neural structure (receptor, nerve or brain tissue) to modulate its activity. Neurosignaling waveforms or Vibes consist of precise algorithms that bias activity of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, so that you can enjoy a shift into a more energetic or relaxed state. Neurosignaling builds upon the best features of long-standing tDCS and TENS techniques by using pulsed currents with lower-intensity and higher-frequency outputs delivered through bio-compatible materials for greater safety and comfort.”[4]
Purpose
Thync is a wearable device that delivers the effects of either a sleeping pill or a double espresso, without any of the drawbacks, in just one 15-minute session.
Company & People
- Isy Goldwasser - CEO and Founder
- Jamie Tyler Ph.D. - CSO and Founder
- Sumon Pal Ph.D. - Chief of Vibes
- Anil Thakur - CTO
- Jason Egnal - VP, Digital Marketing & Commercial Operations[5]
Important Dates
- 2011 - Co-founding of Company Thync by experts in the fields of neurobiology, neuroscience and consumer electronics from institutions that include MIT, Harvard, and Stanford Universities.
- October 2014 - Beginning of the project Thync.
- June 2015 - start selling the device Thync.”[5]
Ethical Issues
Health Risks
There have been no significant issues regarding Thync’s safety profile, according to the company. We do know that many people already engage in alcohol, drugs, and other activities due to stress, anxiety, and mood problems. Thync may allow for a safer way to alleviate these problems.[6]
However, the product is very new, so you can not assume that in the future no health risks to come. Although the technology of neural stimulation of the brain appears to be very dangerous, it is already commonly used for treatment of various diseases. For example:
"Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is the application of electric current through the skin to alleviate pain. Among the simple nonpharmacological means, combining psychological and somatic effects and helps reduce the need for analgesics. Most leads to relief of back pain in the suprapubic and perineal relief is smaller. Induces a placebo effect. TENS is a contraindication pacemaker."[7]
Another example is Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS). Deep brain stimulation is based on the transmission of electrical impulses to the brain using thin electrodes. These lead to the neurostimulator which patients are implanted into the chest. Patients with Parkinson's disease, where failed all available therapies, there is a significant motor improvement. Similarly successful this method in patients with epilepsy, which greatly reduces the frequency of epileptic seizures. However tested in people with psychiatric disorders or obesity, said Milan Brázdil, head of the First Department of Neurology at the University Hospital St. Anna in Brno.[8]
Safety of product Thync also engaged in leading scientific experts, although relevant studies are still missing. This is evidenced eg. Web portal Quora.com. Yates Buckeley (Computational Neuroscience) said:
"When released as a product Thync was explained to be a high frequency current stimulation. Research in this area is new so the mechanism (like most brain things) is not well understood."[9]
The most frequently raised points of confusion:
- most people find it relaxing
- some do not / has some side effects
- not well understood
- long term use unclear
- not a medical device”[9]
Yates also points out that, the recent study found a slight decrease in IQ as a a result of basic electrical stimulation and he is afraid of a possible associating with Thync:
"I presume somehow it reset some connections. I have a slight concern Thync could have a similar effect but this is very hard to test."”[9]
Enhancement/Therapy/Treatment
Public & Media Impact and Presentation
Public Policy
Related Technologies, Project or Scientific Research
References
- ↑ Shows if the device is a standalone wearable computer or if it needs to be connected to a processing unit to function.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Cdr.cz: Thync vypouští do světa headset, který skrz impulzy do mozku ovládá vaši náladu [online]. Copyright © 1998-2015 CDR server s.r.o. [retr. 16.10.2015]. ISSN 1213-2225. Available from: http://cdr.cz/clanek/zprava-thync-vypousti-do-sveta-headset-ktery-skrz-impulzy-do-mozku-ovlada-vasi-naladu
- ↑ Gizmac.com: Thync mood-changing wearable officially launches - we go hands on (again) [online]. All content copyright © Gizmag 2003 - 2015 [retr. 16.10.2015]. Available from: http://www.gizmag.com/thync-hands-on-2/37820/
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Thync.com: Science/Technology [online]. Copyright 2015 Thync [retr. 20.10.2015]. Available from: http://www.thync.com/science-and-technology
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Thync.com: About Us [online]. Copyright 2015 Thync [retr. 16.10.2015]. Available from: http://www.thync.com/about
- ↑ MedTech Boston: Testing Thync: A Calming, Energizing Personal Brain Modulator [online]. ©2013-2016 Medical Networking, Inc. [retr. 8.11.2015]. Available from: https://medtechboston.medstro.com/testing-thync-a-calming-energizing-personal-brain-modulator/
- ↑ PORODNICE.CZ: Transkutánní elektrická nervová stimulace (TENS) [online]. Copyright (c) 2002-2015, Porodnice.cz [retr. 8.11.2015]. Available from: http://lekari.porodnice.cz/transkutanni-elektricka-nervova-stimulace-tens
- ↑ ČT24: "Na operace mozku jsme ideálně připraveni", říká Milan Brázdil [online]. © Česká televize 1996 – 2015 English [retr. 8.11.2015]. Available from: http://www.ceskatelevize.cz/ct24/archiv/1041312-na-operace-mozku-jsme-idealne-pripraveni-rika-milan-brazdil.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Quora.com: What are the potential dangers of brain-zapping devices like Thync? [online]. Quora. com [retr. 8.11.2015]. Available from: https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-potential-dangers-of-brain-zapping-devices-like-Thync